Australian Medical Registration
Let us understand the famously complicated Australian Medical Registration process.
Firstly, like the UK, the expression ‘medical license’ doesn’t invoke much familiarity in Australia. Here also, they are terms like ‘Registration for Medical Practice Australia’ and 'Medical Registration Australia' that make all the sense.
Secondly, to understand Australian Medical Registration, you will need to get acquainted with all the councils and authorities involved. There are quite a few! We will try to sort it out for you a little.
Most importantly, there are some opportunities for International Medical Graduates in Australia. However, there is a pretty formidable challenge too. Don’t forget to read the section on challenges of getting into Australia at the end of the page.
Let’s understand the process of the Medical Board of Australia Registration.
Authorities associated with Medical Registration
Understanding how to get full Medical Registration in Australia begins with awareness. You must gain acquaintance with the various functional units in the process of Medical Registration in Australia.
Moreover, we can safely establish that no other nation has such a round-about, complex array of authorities as does Australia. As a result, you need to put an effort to understand the structure. Consequently, you will understand the process.
To sum up, to become a Doctor in Australia, an IMG (International Medical Graduate) needs to know –
- Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA)
- 15 National Boards
- Medical Board of Australia
- States and Territory Boards & Committees
- Australian Medical Council
In conclusion, we can infer that all these bodies have one ultimate purpose – to try and make sure that quality Medical Services exist for the people living in Australia.
Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA)
In short, AHPRA runs the National Registration and Accreditation Scheme (NRAS)*. The NRAS came into existence through the Health Practitioner Regulation National Law 2009-10. We will explain the NRAS concept below. Read on!
15 National Boards
There are 15 National Boards through which the AHPRA operates. Each National Board is exclusive to one of the 15 Medical Professions. For example, there is a National Board each for Dental, Psychology, Optometry, etc.
Certainly, one of these is the Medical Board of Australia mentioned above which includes all the major disciplines of Allopath.
Medical Board of Australia
Meanwhile, the Australian Medical Board is the principal authority that will finally grant registration to foreign doctors in Australia. In other words, this is the Board that gives you the ‘Medical License Australia’.
Most importantly, when we say Doctors, we mean the mainstream Allopath Doctors. If you are in an ‘offshoot’ Medical profession like Chinese Medicine, Dental, Psychology, etc., there are other National Boards. In the same vein, there are 15 of such in Australia.
In addition, the Medical Board of Australia has numerous other functions. For instance, it hears and investigates complaints about Doctors, makes and enforces codes and guidelines, and supervises accreditation of study courses. Most importantly, the assessment of IMGs who are looking for an opportunity to practice here falls in the purview of this Board.
States and Territory Boards and Committees
The above Board is supported by individual Boards in each State and Territory. Their main function is to carry out the execution of policies put in place by the Medical Board. They have the power to make minor decisions related to individual registrations.
So, if you come across any discrepancy or irregularity in your Registration, the relevant State or Territory Board will hear you first.
Australian Medical Council
In short, the summary of the responsibilities of the Australian Medical Council (AMC) would be the supervision of standards of the education, training, & assessment of the medical professionals.
Moreover, the AMC has numerous other functions. Of these, there is one that you need to know of. The AMC is the supreme authority for the overall assessment of IMGs by managing the Australian Medical Council Exam. That is to say, the AMC conducts the AMC CAT MCQ and the AMC Clinical Examination.
NRAS
The National Registration and Accreditation Scheme is simply the concept of standardizing all Medical Services in Australia. Whichever mode of treatment you wish to follow in Australia, there is a standard of treatment and accountability you can expect. Of course, the mainstream Allopath is the principal pillar the NRAS affects.
The principal purpose of the NRAS is two-fold. Firstly, the NRAS contains the professional standards that the Doctors need to meet to get the Australian Medical Registration.
Secondly, the NRAS brings uniformity. This uniformity makes it possible for the Doctors to work in different provinces without having to get a re-registration. More or less this is what the soon to be erstwhile MCI Screening Test (the upcoming NExT) does for the Indian Medical infrastructure.
Registration for practicing medicine in Australia for IMGs
IMGs are those who have completed their primary medical qualification from a country other than Australia.
We shall begin by briefly introducing the different types of Registration that exist for entering the Australian medical system. To begin with, you may find the following information a bit random. You need to read these along with the section on ‘Assessment Pathways’ that comes immediately after the section on ‘Types of Australian medical registration’.
Types of Australian Medical Registration
Depending upon the qualification and the experience of the Doctors, the Australian medical infrastructure offers different arrangements. These arrangements include different ‘assessment pathways’ leading to different ‘types of Registration’.
Firstly, let us understand the various types of Registration that exist in Australia:
General Registration
Perhaps the broadest and the most relevant (for IMGs) among the medical registration options is the General Medical Registration Australia. The pathway that an IMG needs to take up for General Registration is the Competent Authority Pathway Australia or the Standard Pathway. (Read below)
Specialist Registration
If you are a Specialist and an AMC accredited Specialist College has approved your specialization, you become eligible for the Specialist Registration. As the name suggests, in such cases, you follow the Australian Medical Council Specialist Pathway. (Read below)
Limited Registration
PG or supervised practice –
This is for those IMGs choosing to undergo supervised training either to gain eligibility for General/Specialist Registration or if they wish to prepare for the Australian Medical Council clinical examination.
Special need area –
A Doctor may apply for Registration under the ‘Area of need’ provision. This is when the Doctor finds employment in areas where there is a shortage of medical practitioners. The Assessment Pathway one must follow is either the Standard Pathway or the Specialist Pathway (Special Need).
Peoples’ interest –
Sometimes the Medical Board of Australia can grant limited registration to a Doctor that is short-term and has limited scope of practice. This happens in rare occasions and the Board does it in the interest of the people, like when there is a pandemic or a natural disaster. This is not a good choice if you are looking for a more permanent medical registration in Australia (General or Specialist). The Area of Need Limited Registration is better for this.
Research or Teaching –
Again, as the name suggests, you may get this limited registration for the purpose of continuing research or undertaking teaching at a university, maybe. Again, for obvious reasons, it is not a good choice for those who are looking for General or Specialist Registration.
Non-Practicing Registration
Hardly is this for anyone looking to practice in Australia. It is suitable for those Doctors who have retired or are practicing out of Australia.
Provisional Registration
As the name suggests, it is a temporary registration. This is for those who already have approval for the General Registration but they have to serve under supervision for a period. After they complete this, they get the Full General Registration.
Apart from these, there is a student registration too. When you take up one of the approved medical courses to study, you have to get registered. This course should be one that leads to registration as a medical practitioner.
Assessment Pathways to Australian Medical Practice Registration
As mentioned earlier, there are different Assessment Pathways to check the eligibility of IMGs. To understand, you have to read them with the above section on types of registration.
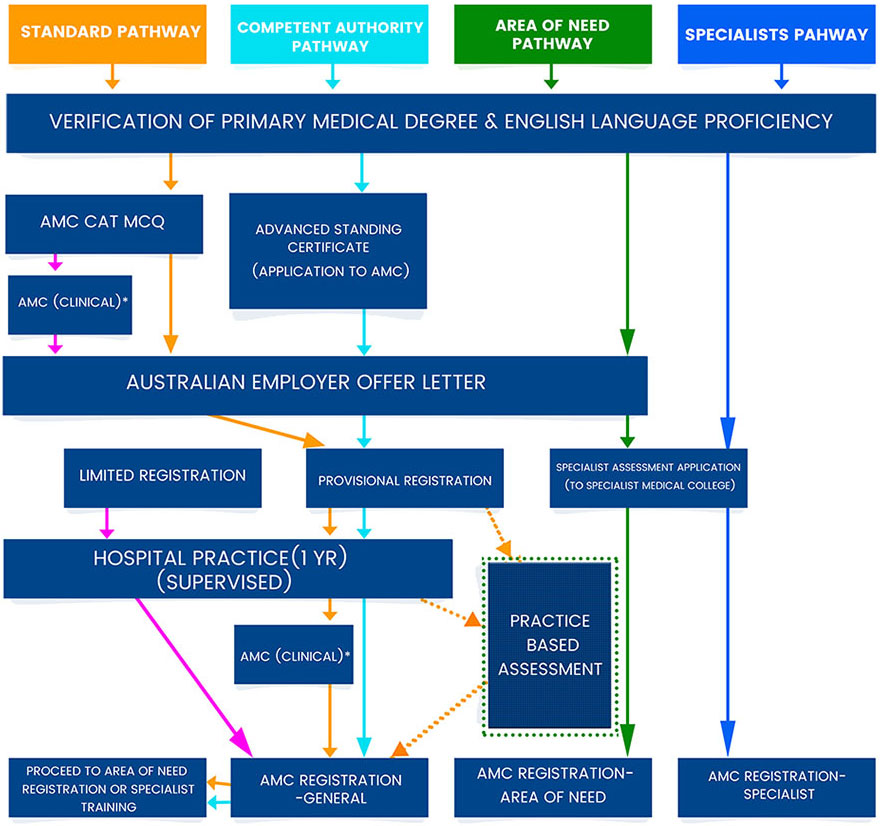
Competent Authority Pathway
Firstly, this pathway is for IMGs who seek General Registration in Australia, whether they are Specialists or not. The only condition being they should have a valid PG from a ‘Competent Authority’.
Now, the Australian Medical Board has approved some international authorities to be competent to assess the eligibility of IMGs to practice. These are called the Competent Authorities. These include –
- GMC UK – IMG must have cleared PLAB or completed a GMC-recognized course in the UK
- If you have LMCC (to be linked with Canada License page)
- ECFMG – IMG must have cleared USMLE
- Medical Councils of New Zealand & Ireland
The clearing of these tests and meeting these eligibility criteria is not the end. The IMG must have requisite training/Residency under these competent authorities. Therefore, an IMG must have a PG degree from these authorities.
To sum up, to get General Registration and thence practice in Australia, you must clear USMLE/PLAB (or UKMLA) and complete your PG from the concerned country (US/UK).
In addition, the candidate must have a primary qualification of standard. That means, the Institute must be accredited by both the Australian Medical Council (AMC) & the World Directory of Medical Schools (WDOMS).
As mentioned above, the first registration an IMG gets through this pathway is Provisional Registration. After 12 months of supervised practice, she qualifies for the General Registration.
Standard Pathway
This is the pathway to follow when an IMG has not cleared USMLE/PLAB (or UKMLA). You do not have to appear in the USMLE/PLAB (UKMLA). But you must clear the AMC CAT MCQ.
The AMC CAT MCQ may be called the Australian Medical Council exam for foreign medical graduates. The clause for the Primary Medical Qualification is same as above.
This is a direct path to enter Australia. There are 2 ‘sub’ paths to it. You may go for clearing the AMC Clinical Examination. This is for the non-Specialist IMGs. Or, after clearing AMC CAT MCQ you let an AMC-recognized authority to assess your knowledge and skills as you work under its supervision. The latter is a less frequently chosen option.
Now, let us relate this to the Limited Registration and Provisional Registration mentioned above. Those IMGs who clear AMC CAT MCQ may apply for limited registration. Then, they go for supervised practice.
IMGs who clear both the AMC CAT MCQ & the AMC Clinical Examination are eligible to apply for the Provisional Registration.
Eventually, both these IMGs become eligible to apply for Full General Registration after they do the needful in their respective positions.
Specialist Pathway
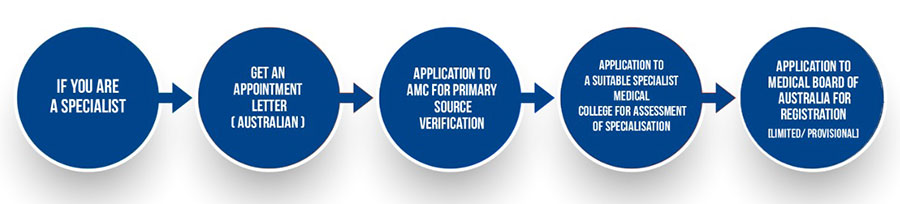
When an IMG is a Specialist, two paths exist in the Australian Medical Council Specialist Pathway.
Specialist Pathway – Specialist Recognition – The Specialist subjects her Specialist Training to a comparative analysis. The comparison is with a Specialist trained in the same discipline in Australia. A Specialist Medical College assesses this. This assessment happens through the conduction of a supervised practice association.
Specialist Pathway – Area of need – the Specialist applies for an ‘area of need’ position under a Specialist Medical College. The relevant state authority determines the area of need.
The Area of need pathway does not lead to Specialist Registration. The Specialist Recognition Pathway does. However, the former can also be on the latter pathway, if they so wish.
This is a summary of the Australian Medical Council Registration for foreign doctors. To sum up, an Indian MBBS, the requirements to practice medicine in Australia include –
MBBS from a college that features in WDOMS
Clearing either USMLE or PLAB (UKMLA) or AMC CAT MCQ
Challenges of getting into Australia
There are certain facts that an IMG must keep in mind when she makes a decision regarding practicing in Australia.
The Australian Medical Council Exam, AMC CAT MCQ, is indeed a notoriously difficult examination to clear. As per statistics, the success rate of the aspirants is astoundingly low. Only 28% of the Doctors appearing in this test succeed.
On the other hand, the success rate in the USMLE is as high as 66%.
In fact, the Australian Medical Council Exam for foreign medical graduates is so tough that most Indian Doctors don’t even start the Australian Medical Council Exam preparation.
Another concern is the Australian Medical Council Exam fees. Many aspirants resent the fact that they have to invest an amount to the tune of 3, 33, 000 INR for an exam they are almost sure not to succeed in.
Ideal way to enter into Australian Healthcare system
In conclusion, if you wish to make a career in medicine in Australia, you have 2 options:
Conventional Agents: You will find a lot of agents around you promoting medical careers in Australia. Almost all of these agents are actually promoting a lesser known ‘non-clinical’ pathway. If a non-clinical career is what you are looking for, you may invest 70 lacs - 1 Crore and enter into the Australian system. Of course, you won’t be practicing then. However, if you have a long term plan to practice clinically in Australia, we strongly advise you to reconsider your decision.
Moksh Pathway : If you wish to settle in Australia and have a clinical practice, you need to pursue PG either in India or USA. After that, you may apply in Australia to work clinically through the AMC Australia Specialist Pathway. However, you need to do 2 things for this.
Firstly, you need to prepare for the AMC CAT MCQ. Your best bet to clear this tough exam is preparing with Moksh. Secondly, you need to associate with an immigration agent for Australia and, when the time comes, apply for immigration to Australia. Just make sure that the immigration agent is licensed. Keep in mind, due to the competition and the quota system in Australia, not many seats are available for PG here.
Speak to MOKSH Counselor to understand further.



